Home
 10 Pillars 10 Pillars  Map Map  Tree Tree
 Rationale Rationale
 Forum Forum
 About About
 Terms Terms
 Contact Contact
|
Search
top academic & professional resources |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Pillar 1: Foundations Chaim Zins |
Loading
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
It explores the philosophical, sociological, historical, methodological, and mediating perspectives of human knowledge itself.
 Field En Encyclopedic article M Media (images, videos, virtual tours) C Course R Information resources
Field En Encyclopedic article M Media (images, videos, virtual tours) C Course R Information resources  ©
©
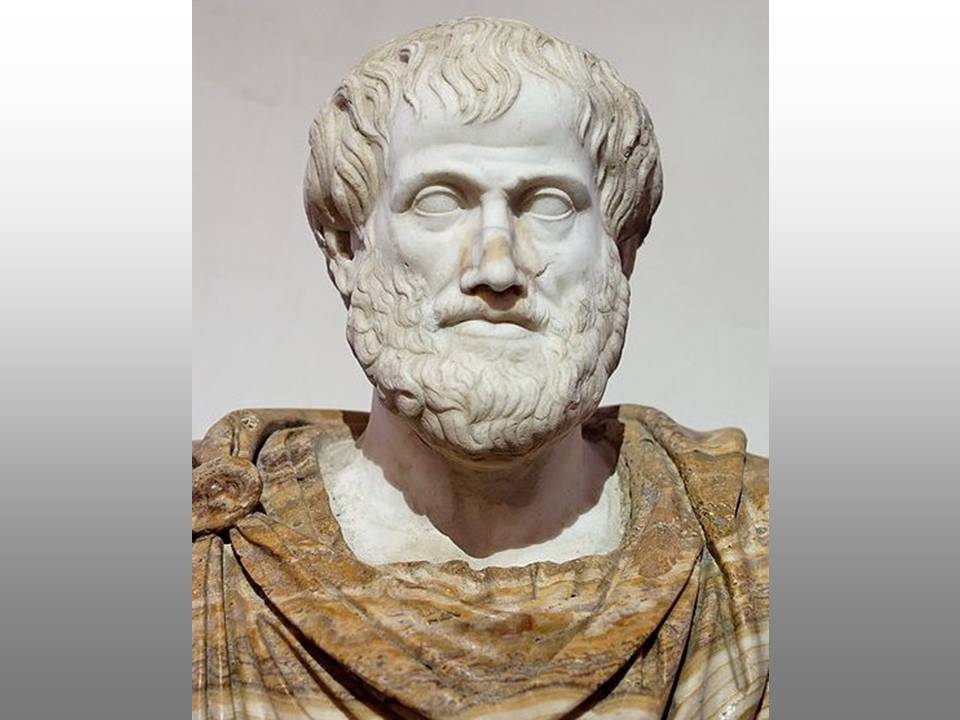 © 1.
Theory (1)
© 1.
Theory (1) studies the philosophical aspects of knowledge and science.
 Philosophy
of knowledge (Epistemology)
Philosophy
of knowledge (Epistemology) = The study of the philosophical aspects of knowledge.
En Epistemology (W); (SEP);
» Knowledge (W); (SEP);
» Trouth (W); (SEP).
M Best of 3D Street Art Illusions (YouTube).
» Magic's Secrets Revealed (YouTube). (43:03).
» Animal Planet: Mermaids (Discovery) / It's a Hoax (CNN).
A mockumentary on mermaids.
M The Dark Secret of Hendrik Schoen (BBC). on YouTube.
A documentary on the scientific scandal. (48:03).
 Philosophy
of science
Philosophy
of science= The study of the philosophical aspects of science.
En Philosophy of science (W)
» Science (W); (SEP).
M Science Under Attack (BBC) on YouTube (53:39).
 © 2.
Context
(Place & Time) (2)
© 2.
Context
(Place & Time) (2)studies the historical and sociological aspects of knowledge.
 History
of science
History
of science= The study of the history of all sciences.
En History of science (W)
 Sociology
of knowledge
Sociology
of knowledge= The study of the social aspects of thought and science.
En Sociology of knowledge (W)
 © 3.
Methodology
(3)
© 3.
Methodology
(3)studies the methodological aspects of scientific research
 Methodology of science
Methodology of science= The study of research methodologies.
En Methodology of science (W)
 © 4. Mediation (4)
© 4. Mediation (4)studies the mediating aspects of knowledge
 Information science
Information science= The study of the ways to connect knowlege and users.
En Information science (W)
M Art of Data Visualization (PBS) (7:44).
 Museology
Museology= The study of the organization of museums and exhibitions.
En Museology
 Scientometrics
Scientometrics= The study of science by statistical-based methodologies*.
En Scientometrics (W)
a must for your library
| 中 文 English Français Deutsch עברית 日 本語 नेपाली Polski Português Română русский Српски Español More.... |
a must for your library
Chaim Zins, Knowledge Mapping Research, 26 Hahaganah St. Jerusalem, 97852 tel: 972-2-5816705 chaim.zins@gmail.com